「Pythonで3Dデータを扱いたい」
「Pythonで高速に3D画像を処理したい」
「3Dデータを用いた機械学習を試したい」
このような場合には、Open3Dがオススメです。
この記事では、Open3Dについて解説しています。
本記事の内容
- Open3Dとは?
- Open3Dのシステム要件
- Open3Dのインストール
- Open3Dの動作確認
それでは、上記に沿って解説していきます。
Open3Dとは?
Open3Dとは、3Dデータを扱うオープンソースのPythonライブラリです。
Open3Dの特徴は、以下が公式で主張されています。
- 3D data structures
- 3D data processing algorithms
- Scene reconstruction
- Surface alignment
- 3D visualization
- Physically based rendering (PBR)
- 3D machine learning support with PyTorch and TensorFlow
- GPU acceleration for core 3D operations
- Available in C++ and Python
英語のままの方が、わかりやす部分があるでしょう。
「Surface alignment」なんて、対応する日本語がありません。
上記の特徴は要するに、次のことを言っています。
- PythonとC++から操作が可能
- 物理ベースレンダリングによるリアルな3D表現
- 3D機械学習への対応
- GPUによる処理の高速化
まさに時代が求めている機能です。
Open3Dは、今後メタバース関連での利用が進むかもしれませんね。
以上、Open3Dのついて説明しました。
次は、Open3Dのシステム要件を確認します。
Open3Dのシステム要件
現時点(2022年2月)でのOpen3Dの最新バージョンは、0.14.1となります。
この最新バージョンは、2021年12月3日にリリースされています。
サポートOSに関しては、以下を含むクロスプラットフォーム対応です。
- Windows
- macOS
- Linux
サポート対象となるPythonのバージョンは、以下となっています。
- Python 3.6
- Python 3.7
- Python 3.8
- Python 3.9
通常、Python 3.6で動けば、それ以降のバージョンでも動きます。
今だと、Python 3.10系が最新バージョンです。
そのため、次のバージョンでもインストールは可能だと考えます。
$ python -V Python 3.10.2
しかし、上記のPythonバージョンだとインストールでエラーが出てしまいます。
ERROR: Could not find a version that satisfies the requirement open3d (from versions: none) ERROR: No matching distribution found for open3d
Pythonライブラリについては、多くのライブラリをインストールしてきました。
しかし、このようなケースはかなり珍しいです。
Open3Dは、Pythonのバージョンをかなり厳格に見ているということでしょう。
でも、それなら次のPython公式開発サイクルには対応して欲しいですね。
| バージョン | リリース日 | サポート期限 |
| 3.6 | 2016年12月23日 | 2021年12月23日 |
| 3.7 | 2018年6月27日 | 2023年6月27日 |
| 3.8 | 2019年10月14日 | 2024年10月 |
| 3.9 | 2020年10月5日 | 2025年10月 |
| 3.10 | 2021年10月4日 | 2026年10月 |
ここは、次の最新バージョンに期待しておきましょう。
とにかく、Pythonのバージョンには従う必要があるということです。
以上、Open3Dのシステム要件を説明しました。
次は、Open3Dのインストールを行います。
Open3Dのインストール
検証は、次のバージョンのPythonで行います。
$ python -V Python 3.8.10
また、公式ではPython仮想環境へのインストールが推奨されています。
後述していますが、依存パッケージが数がかなり多いです。
Python仮想環境については、次の記事でまとめています。
まずは、現状のインストール済みパッケージを確認しておきます。
$ pip list Package Version ---------- ------- pip 22.0.3 setuptools 60.8.1 wheel 0.36.2
次にするべきことは、pipとsetuptoolsの更新です。
pipコマンドを使う場合、常に以下のコマンドを実行しておきましょう。
python -m pip install --upgrade pip setuptools
では、Open3Dのインストールです。
Open3Dのインストールは、以下のコマンドとなります。
pip install open3d
インストールには、かなりの時間がかかります。
焦らずに気長に待ちましょう。
終了したら、どんなパッケージがインストールされたのかを確認します。
$ pip list Package Version -------------------- --------- addict 2.4.0 anyio 3.5.0 argon2-cffi 21.3.0 argon2-cffi-bindings 21.2.0 asttokens 2.0.5 attrs 21.4.0 Babel 2.9.1 backcall 0.2.0 black 22.1.0 bleach 4.1.0 certifi 2021.10.8 cffi 1.15.0 charset-normalizer 2.0.11 click 8.0.3 cycler 0.11.0 debugpy 1.5.1 decorator 5.1.1 defusedxml 0.7.1 deprecation 2.1.0 entrypoints 0.4 executing 0.8.2 fonttools 4.29.1 idna 3.3 importlib-resources 5.4.0 ipykernel 6.8.0 ipython 8.0.1 ipython-genutils 0.2.0 ipywidgets 7.6.5 jedi 0.18.1 Jinja2 3.0.3 joblib 1.1.0 json5 0.9.6 jsonschema 4.4.0 jupyter-client 7.1.2 jupyter-core 4.9.1 jupyter-packaging 0.11.1 jupyter-server 1.13.5 jupyterlab 3.2.9 jupyterlab-pygments 0.1.2 jupyterlab-server 2.10.3 jupyterlab-widgets 1.0.2 kiwisolver 1.3.2 MarkupSafe 2.0.1 matplotlib 3.5.1 matplotlib-inline 0.1.3 mistune 0.8.4 mypy-extensions 0.4.3 nbclassic 0.3.5 nbclient 0.5.10 nbconvert 6.4.1 nbformat 5.1.3 nest-asyncio 1.5.4 notebook 6.4.8 numpy 1.22.2 open3d 0.14.1 packaging 21.3 pandas 1.4.0 pandocfilters 1.5.0 parso 0.8.3 pathspec 0.9.0 pexpect 4.8.0 pickleshare 0.7.5 Pillow 9.0.1 pip 22.0.3 platformdirs 2.4.1 prometheus-client 0.13.1 prompt-toolkit 3.0.26 ptyprocess 0.7.0 pure-eval 0.2.2 pycparser 2.21 Pygments 2.11.2 pyparsing 3.0.7 pyrsistent 0.18.1 python-dateutil 2.8.2 pytz 2021.3 PyYAML 6.0 pyzmq 22.3.0 requests 2.27.1 scikit-learn 1.0.2 scipy 1.8.0 Send2Trash 1.8.0 setuptools 60.8.1 six 1.16.0 sniffio 1.2.0 stack-data 0.1.4 terminado 0.13.1 testpath 0.5.0 threadpoolctl 3.1.0 tomli 2.0.0 tomlkit 0.9.0 tornado 6.1 tqdm 4.62.3 traitlets 5.1.1 typing_extensions 4.0.1 urllib3 1.26.8 wcwidth 0.2.5 webencodings 0.5.1 websocket-client 1.2.3 wheel 0.36.2 widgetsnbextension 3.5.2 zipp 3.7.0
過去最高レベルのパッケージ数かもしれません。
それほど、Open3Dには依存関係のあるパッケージが多いということです。
すでに述べましたが、やはりPython仮想環境を利用すべきでしょうね。
おそらく、既存環境への導入はかなりハードルが高いはずです。
なお、インストールの確認は次のコマンドで可能です。
公式では、この確認方法が記載されています。
python -c "import open3d as o3d"
何もエラーが出なければ、Open3Dのインストールは成功です。
エラーが出た場合は、次のコマンドで詳細を確認することになります。
python -W default -c "import open3d as o3d"
以上、Open3Dのインストールを説明しました。
次は、Open3Dの動作確認を行います。
Open3Dの動作確認
サンプルは、以下で公開されています。
https://github.com/isl-org/Open3D/tree/master/examples/python
その中から、シンプルなコードを選びます。
visualization/line_width.py
import open3d as o3d
import random
NUM_LINES = 10
def random_point():
return [5 * random.random(), 5 * random.random(), 5 * random.random()]
def main():
pts = [random_point() for _ in range(0, 2 * NUM_LINES)]
line_indices = [[2 * i, 2 * i + 1] for i in range(0, NUM_LINES)]
colors = [[0.0, 0.0, 0.0] for _ in range(0, NUM_LINES)]
lines = o3d.geometry.LineSet()
lines.points = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(pts)
lines.lines = o3d.utility.Vector2iVector(line_indices)
# The default color of the lines is white, which will be invisible on the
# default white background. So we either need to set the color of the lines
# or the base_color of the material.
lines.colors = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(colors)
# Some platforms do not require OpenGL implementations to support wide lines,
# so the renderer requires a custom shader to implement this: "unlitLine".
# The line_width field is only used by this shader; all other shaders ignore
# it.
mat = o3d.visualization.rendering.MaterialRecord()
mat.shader = "unlitLine"
mat.line_width = 10 # note that this is scaled with respect to pixels,
# so will give different results depending on the
# scaling values of your system
o3d.visualization.draw({
"name": "lines",
"geometry": lines,
"material": mat
})
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
上記コードを実行すると、次のような画面が表示されます。
環境によっては、時間がかかる場合もあるでしょう。
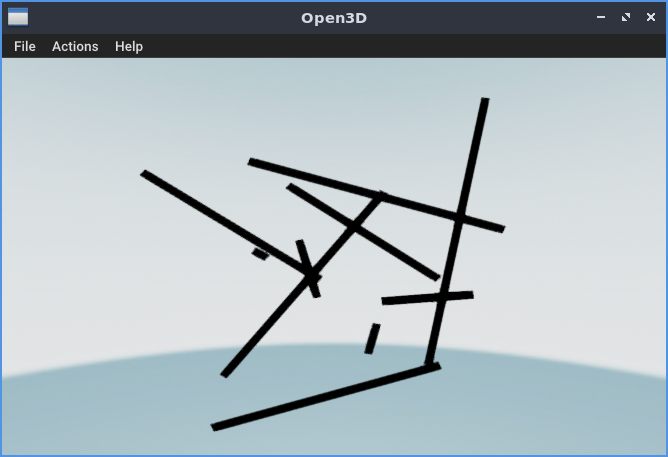
画面内をマウスでグリグリと動かすことが可能です。
単純なコードですが、ちゃんとした3Dが表示されています。
これで、Open3Dの動作確認としては十分でしょう。
あとは、サンプルをダウンロードして見ていくだけです。
習うより慣れろの精神でサンプルコードを漁っていきましょう。
以上、Open3Dの動作確認を説明しました。





